JavaScript 实现字节单位转换 —— Byte 转 KB、MB、GB、TB ...
背景
将字节(Bytes)转成 KB、MB、GB、TB 等,是十分常见的需求,它的实现方法有多种,本文列出了常见的四种实现,最推荐的是第4种:BigInt 版。
方法1:if else
一般做法是,通过判断 bytes / 1024 是否大于 1024,来决定是否提升单位:
function formatBytes(bytes: number) {
const K = 1024;
if (bytes < K) {
return `${bytes} B`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} KB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} MB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} MB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} GB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} TB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} PB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} EB`;
} else if ((bytes /= K) < K) {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} ZB`;
} else {
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} YB`;
}
}
formatBytes(1024 * 1024); // "1.00 MB"(bytes /= K) < K 是一个简写,等同于:
bytes = bytes / K;
if (bytes < K) {
// ...
}通过 if-else 实现略显繁琐,下面我们将用 while 循环改写。
方法2:while
function formatBytes(bytes: number) {
if (bytes === 0) {
return "0 B";
}
const sizes = ["B", "KB", "MB", "GB", "TB", "PB", "EB", "ZB", "YB"];
const K = 1024;
let i = 0;
while (bytes >= 1024 && i < sizes.length - 1) {
bytes /= K;
i++;
}
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} ${sizes[i]}`;
}
formatBytes(1024 * 1024); // "1.00 MB"方法3:Math.log
相比 if-else,使用 while 会“清爽”许多,但还有更好的方法:Math.log:
function formatBytes(bytes: number) {
if (bytes === 0) {
return "0 B";
}
const sizes = ["B", "KB", "MB", "GB", "TB", "PB", "EB", "ZB", "YB"];
const K = 1024;
const i = Math.floor(Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(K));
bytes /= Math.pow(K, i);
return `${bytes.toFixed(2)} ${sizes[i]}`;
}
formatBytes(1024 * 1024); // "1.00 MB"相比 while,Math.log 在常数时间(O(logn))内完成,通过对数计算直接得到 i,显得更加“高级”。
对数运算是指数运算的“逆运算”,我们想要得到的 i,本质上,是获取以 K 为底,bytes 的对数,然后再向下取整,得到在 sizes 中对应的下标。
由于 JavaScript 没有提供计算任意底数的指数方法,所以用到了指数“换底公式”:
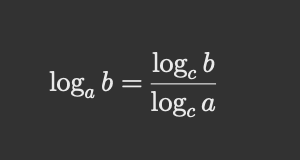
Math.log 是 JavaScript 中求自然对数的内置方法,通过 Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(K) 可以获取到目标单位的索引(下标)。
限制有效范围
到目前为止,我们的 formatBytes 函数还没有对参数进行限制,虽然有 TypeScript 的约束,但它只在开发阶段有效,并且无法判断参数是否为非负整数,所以补充以下代码:
function formatBytes(bytes: number) {
// 当 bytes 不是非负整数,或者 bytes 大于 2 ** 53 - 1 时,抛出一个异常
if (
!(Number.isInteger(bytes) && bytes >= 0 && bytes <= Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
) {
throw new Error(
"Invalid input: `bytes` must be a non-negative integer within Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER",
);
}
// ...
}
formatBytes(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER); // "8.00 PB"
formatBytes(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1); // ErrorNumber.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER 是一个常量,等同于 2 的 53 次方减 1,这是 JavaScript 能够精确计算的最大整数,对应还有 Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER,表示 JavaScript 能够精确计算的最小整数:
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER === Math.pow(2, 53) - 1; // true
Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER === -(2 ** 53 - 1); // true方法 4: BigInt(推荐)
如果你足够细心,会发现我们的 formatBytes 能够处理的最大数量大约是 8.00 PB,也就是 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER 个字节,再大就会丢失精度:
2 ** 53 - 1; // 正常 9007199254740991
2 ** 53; // 正常 9007199254740992
2 ** 53 + 1; // 异常:9007199254740992
2 ** 53 + 2; // 异常:9007199254740994这个问题并不常见,因为 8.00 PB 已经非常大了,足够日常使用,如果还要支持更大的数量级,可以用 ES2020 引入的基础数据类型:BigInt,下面是改写后的代码:
function formatBytes(bytes: string | bigint | number) {
try {
bytes = BigInt(bytes);
if (bytes < 0n) {
throw new Error();
}
} catch {
throw new Error(
"Invalid input: `bytes` must be an integer, BigInt, or an integer string, and they all must be non-negative",
);
}
if (bytes === 0n) {
return "0 B";
}
const sizes = ["B", "KB", "MB", "GB", "TB", "PB", "EB", "ZB", "YB"]; // 等等 ...
const K = 1024n;
let i = 0n;
const originBytes = bytes;
while (bytes >= K && i < sizes.length - 1) {
bytes /= K;
i++;
}
const intPart = bytes;
const level = K ** i;
const decimalPart = originBytes - level * intPart;
const num = Number(intPart) + Number((decimalPart * 1000n) / level) / 1000;
if (num > Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) {
throw new Error(
`Invalid input: \`bytes\` exceeds the maximum precise value that ${
sizes[sizes.length - 1]
} can represent`,
);
}
return `${num.toFixed(2)} ${sizes[Number(i)]}`;
}
// formatBytes(1024n ** 8n * BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)); // 9007199254740991.00 YB
// formatBytes(1024n ** 8n * BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1)); // Error注意:
- Math.log() 不支持传入 BigInt,所以选择用 while 实现;
- 由于 bigint 做除法会自动省略(不是四舍五入)小数部分,所以代码中单独对小数部分进行处理;
- 当 bytes 大到连 YB 量级都超过 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER 时,会触发一个报错,如果不想报错,可以往 sizes 中追加比 YB 更高数量级的单位;
这种方法较为理想,因为不受浮点数精度的影响,无最大值限制。
